HOLLYWOOD ELIXIR™
Walkthrough of the formulated ingredients.
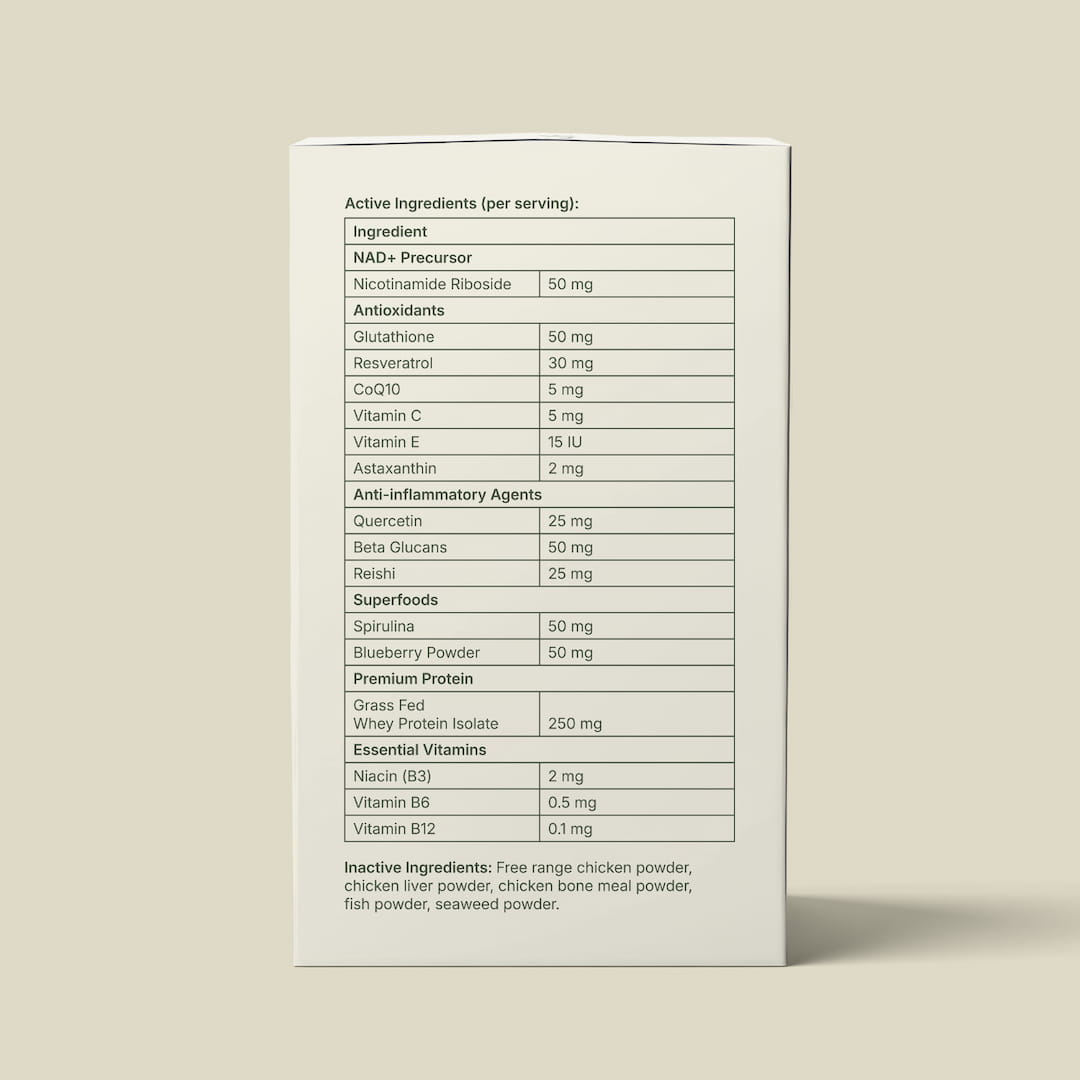
NAD+ PRECURSORS
NAD+ precursors like Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) are essential for enhancing cellular energy and metabolic function in cats and dogs. As pets age, NAD+ levels decline, leading to diminished vitality and increased susceptibility to age-related diseases. NR helps replenish these levels, thereby supporting mitochondrial function and promoting energy production at the cellular level. By improving cellular metabolism, NR can enhance overall wellness, support anti-aging processes, and contribute to a stronger immune system, ensuring pets remain active and healthy throughout their lives.
→ Links:
ANTIOXIDANTS
Antioxidants are crucial for combating oxidative stress and protecting cellular health in pets. Glutathione, a powerful intracellular antioxidant commonly called "the mother of all antioxidants", neutralizes harmful free radicals and supports detoxification processes. Resveratrol, found in grape skins, offers cardioprotective benefits and promotes longevity. CoQ10, essential for mitochondrial function, enhances cellular energy production and protects against oxidative damage. Vitamin C and Vitamin E work synergistically to protect cell membranes and DNA from oxidative stress, while Astaxanthin, a potent carotenoid, offers superior antioxidant protection. Together, these antioxidants help mitigate the effects of aging, support immune function, and maintain overall cellular health in cats and dogs.
→ Links:
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY AGENTS
Anti-inflammatory agents are vital for reducing chronic inflammation and supporting joint health in pets. Quercetin, a flavonoid found in many plants, possesses strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Beta Glucans, derived from yeast and fungi, modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation. Reishi, a medicinal mushroom, offers both anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting benefits. These agents help alleviate joint pain, reduce the risk of inflammatory diseases, and enhance overall wellness in cats and dogs, promoting a more active and comfortable life.
→ Links:
SUPERFOODS
Superfoods provide a dense concentration of nutrients that support overall health and vitality in pets. Spirulina, a blue-green algae, is rich in proteins, vitamins, and antioxidants, promoting immune function and detoxification. Blueberry powder, packed with antioxidants and vitamins, supports cognitive function and combats oxidative stress. Incorporating these superfoods into a pet's diet helps boost their immune system, protect against oxidative damage, and enhance overall health and longevity.
→ Links:
PREMIUM PROTEIN
Premium protein sources like Grass Fed Whey Protein Isolate are essential for muscle maintenance and overall health in pets. This high-quality protein provides all the essential amino acids required for muscle repair, growth, and immune function. Derived from grass-fed cows, this protein is free from artificial additives and hormones, ensuring a clean and natural source of nutrition. Adequate protein intake supports lean muscle mass, enhances recovery from exercise, and promotes a healthy immune system, contributing to the overall vitality and well-being of cats and dogs.
→ Links:
ESSENTIAL VITAMINS
Essential vitamins are crucial for various metabolic processes and overall health in pets. Niacin (B3) supports energy metabolism and maintains healthy skin and coat. Vitamin B6 is vital for amino acid metabolism, neurotransmitter synthesis, and red blood cell production. Vitamin B12 is essential for neurological function, DNA synthesis, and the formation of red blood cells. Together, these vitamins ensure that pets maintain optimal metabolic function, support neurological health, and promote a healthy immune system, contributing to their overall wellness and longevity.
→ Links:
REFERENCES
[1] Lobo V, Patil A, Phatak A, Chandra N (2010) Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: impact on human health. Pharmacogn Rev 4:118–126
[2] Ashok BT, Ali R. The aging paradox: Free radical theory of aging.Exp Gerontol.1999;34:293–303.
[3] Cantuti-Castelvetri I, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph JA. Neurobehavioral aspects of antioxidants in aging.Int J Dev Neurosci.2000;18:367–81.
[4] Yang H, Leng J, Liu N, Huang L. Editorial: Free radicals and antioxidants in diseases associated with immune dysfunction, inflammatory process, and aberrant metabolism. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 16;15:1363854. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1363854. PMID: 38298379; PMCID: PMC10825471.
[5] Ebadi M.Antioxidants and free radicals in health and disease: An introduction to reactive oxygen species, oxidative injury, neuronal cell death and therapy in neurodegenerative diseases.Arizona: Prominent Press; 2001.
[6] Peoples JN, Saraf A, Ghazal N, Pham TT, Kwong JQ. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in heart disease. Exp Mol Med. 2019 Dec 19;51(12):1-13. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0355-7. PMID: 31857574; PMCID: PMC6923355.
[7] Cholia R.P., Kumari S., Kumar S., Kaur M., Kaur M., Kumar R., Dhiman M., Mantha A.K. An in vitro study ascertaining the role of H2O2 and glucose oxidase in modulation of antioxidant potential and cancer cell survival mechanisms in glioblastoma U-87 MG cells.Metab. Brain Dis.2017;32:1705–1716. doi: 10.1007/s11011-017-0057-6.
[8] Bentz B. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma as a model of oxidative-stress and cancer.J. Surg. Oncol.2007;96:190–191. doi: 10.1002/jso.20817.
[9] Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M. Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact. 2006 Mar 10;160(1):1-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2005.12.009. Epub 2006 Jan 23. PMID: 16430879.
[10] Lautrup S, Hou Y, Fang EF, Bohr VA. Roles of NAD+in Health and Aging. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2024 Jan 2;14(1):a041193. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041193. PMID: 37848251; PMCID: PMC10759992.
[11] Navas LE, Carnero A. NAD+metabolism, stemness, the immune response, and cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Jan 1;6(1):2. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00354-w. PMID: 33384409; PMCID: PMC7775471.
[12] Lautrup S, Sinclair DA, Mattson MP, Fang EF. NAD+in Brain Aging and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cell Metab. 2019 Oct 1;30(4):630-655. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.09.001. PMID: 31577933; PMCID: PMC6787556.
[13] Wang X, He HJ, Xiong X, Zhou S, Wang WW, Feng L, Han R, Xie CL. NAD+in Alzheimer's Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Systematic Therapeutic Evidence Obtainedin vivo. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 3;9:668491. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.668491. PMID: 34414179; PMCID: PMC8369418.
[14] Perez-Sanchez C, Escudero-Contreras A, Cerdó T, Sánchez-Mendoza LM, Llamas-Urbano A, la Rosa IA, Pérez-Rodriguez M, Muñoz-Barrera L, Del Carmen Abalos-Aguilera M, Barbarroja N, Calvo J, Ortega-Castro R, Ruiz-Vilchez D, Moreno JA, Burón MI, González-Reyes JA, Collantes-Estevez E, Lopez-Pedrera C, Villalba JM. Preclinical Characterization of Pharmacologic NAD+Boosting as a Promising Therapeutic Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023 Oct;75(10):1749-1761. doi: 10.1002/art.42528. Epub 2023 Jul 28. PMID: 37094367.
Hollywood Elixir™ — A Lifetime of Love